Tapered Roller Bearings Engineering Data
Tapered Roller Bearings
For more details and a current listing of parts, please visit: Tapered Roller Bearings
Heavy Duty Trucks
At Tyson®, we have supplied the transportation market with tapered roller bearings for over 70 years. Our extensive experience with OEM truck and component manufacturers has placed us at the forefront of changing technologies within the transportation market. Additionally, we continue to supply various aftermarket customers who market our product under their own brand name. Working with these customers has allowed us to gain insight into the needs of the replacement market. Whether the bearing is for wheel end, a differential or a pinion application, or the vehicle is used for transporting goods, people, or for use in severe duty environments, Tyson® products are built to perform to maximum levels.
- Tyson® Bearings are competitively priced
- Our high-quality bearings are produced to ABMA standards
- Tyson® Bearings are made in the US
- Domestic facilities eliminate long supply lines
- Excellent stock levels on all popular sizes
- Unrivaled customer service to help you get the right bearing for the job
Heavy Duty Applications
There are several applications in a heavy duty truck that use tapered roller bearings.
Wheel End - Tapered roller bearings are found in the wheel ends of your heavy duty truck. They are used in steer axles, drive axles, pusher axles, tag axles and trailer wheel ends. Most of these designs use an inner and outer tapered bearing, but there are a few truck models that use a cartridge or hub unit design.

Differential and Pinion Applications - Tapered roller bearings are also found in the differential and pinion application of your heavy duty truck. The differential and pinion applications require the highest quality product available for severe duty. Tyson® only provides a case carburized product, including advanced geometries for these applications.
Repair Procedures
There are many items to be aware of when changing the bearings of a truck. Always refer to the service manual and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations prior to servicing your heavy duty truck.
For the purpose of providing a level of guidance to change the wheel bearings there are publications put out by the Technology & Maintenance Council. The most common document, RP 618, provides the procedural guidelines for setting wheel end clearance. This document explains in detail all the different parts involved, along with detailed procedures required to obtain the optimal wheel clearance of .001” to .005”.
Below is a link to the Technology & Maintenance website that will provide you with detailed information to change wheel bearings as well as many other maintenance procedures. These are good resources and should be used as guidelines whenever you are servicing your heavy duty truck.
The Technology and Maintenance Council website address is listed below.
https://www.trucking.org/technology-maintenance-council
The Technology and Maintenance Council website address leading to RP618 is listed below.
https://tmc.trucking.org/TMC-Recommended-Practices
Engineering Data
The technical data presented in this section provides a greater understanding of the Tyson® capabilities. It also allows you to select the correct bearings and estimate their performance for a wide range of applications. These calculations apply to the Tyson® selection of tapered roller bearing cups and cones.
Purpose of Tapered Roller Bearings
Tapered roller bearings are bearings that can take both axial loads (sideways or thrust forces), as well as radial loads (downward force). Looking at the diagram below, the bearing angle determines how much axial and radial load the bearing can sustain.

Looking at the diagram below, the inner and outer ring raceways are segments that are made with a taper. This is done so that the conical surfaces of the raceways and the roller axes if projected, will all meet at a common point, or apex, on the main axis of the bearing.
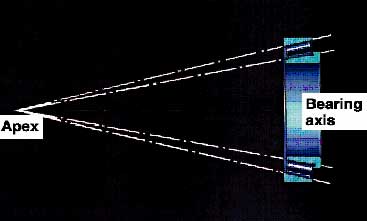
The conical geometry in the bearing uses line contact, which permits greater loads to be carried than with a point contact (ball) bearing. The rollers are guided by a flange on the back of the inner ring (See Components of a Tapered Roller Bearing). This stops the rollers from sliding out at high speed due to their momentum. The larger the half angles of these cones, the greater the axial load the bearing can sustain.
In wheel bearing applications, both radial and axial loads are present. The weight of the vehicle creates the downward load, which is the radial load. The axial load, or thrust load, is created by the turning of the vehicle.
Components of a Tapered Roller Bearing
Tapered roller bearings consist of 2 basic components: the cup and the cone assembly. The cup is the outer ring and is a separate component. The cone assembly is made up of the inner ring, rollers, and the cage.

Tapered Roller Bearing Terminology
Within the cup/cone assembly there are many other terms used to define the various elements of the product. Below is a diagram which labels the various parts of the cup and cone. Each of these elements are important in the design and manufacture of the product.

Design Capabilities
Tyson® Bearings has been designing and manufacturing bearings for over 75 years. We use various advanced modeling methods to determine the best design for your application.
Some of the capabilities and tools used are listed below:
- Design programs and tools
- Harris Bearing Analysis
- “Genrol” Bearing Analysis
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
- MathCAD (over 120 programs)
- Capacity
- Equivalent load
- Contact stress
- Load distribution
- Tapered roller bearings and ball bearing analysis
- Gear forces
Material Information
Tapered roller bearings come in two basic materials: through hardened and case carburized. Each material consists of a combination of alloys which result in specific characteristics needed for these types of products. The choice of which one you use should be driven from the demands of the specific application.
Tyson® primarily offers bearings with case carburized material due to the applications served in the primary market for our products. However, Tyson® can manufacture through hardened material product if the application is best suited for it.
Case carburized bearings are produced by infusing carbon into the outer surface of low carbon steel. The bearing component is then heat treated to give the bearing a hard outer shell and a softer ductile center.
The advantage of using case carburized bearings is that the product has better performance when operating in a dirty or tough environment, and where shock loads are present. Another advantage of case carburized bearings is the compressive residual stresses generated during this heat treat process. This provides the bearing with improved fatigue properties along with the capability of controlling crack propagation. This allows the operator to change out the bearing on a more scheduled approach.
Through hardened bearings are made up of high carbon steel and are hardened consistently throughout the bearing. Because of this, through hardened bearings are more rigid and are more susceptible to cracking under high shock load conditions. That being said, there are several applications in which a through hardened bearing would be adequate for use.
The material, regardless of whether it is through hardened or case carburized, must meet the specifications in which it is being produced. This is especially important when considering the oxygen content of the steel. If the oxygen content is too high, then the result is a shortened life expectancy through subsurface contamination.
Purchasing product produced by proven manufacturers, such as Tyson® Bearings, provides you and your customers with the level of quality required to meet performance expectations.
Lubrication Recommendations
Each application has its own specific lubrication requirements. Always refer to the service manual and follow the manufacturer’s recommendations prior to servicing your heavy duty truck. Tyson® tapered roller bearings come from the factory with a light coat of preservative designed to keep the bearings from rusting. It does not provide adequate operating lubrication. The bearings must either be thoroughly greased or immersed in the oil used in oil bath lubrication before assembly. The bearings and lubricant must be kept clean through the installation process. It is not necessary to remove the preservative coating before installation as long as the bearing is kept clean. We also suggest that different lubricant types (oils and greases) not be mixed.

 Shop Now!
Shop Now!